Dental Caries & Cavities
About Cavities, Caries, and Tooth Decay
What is Dental Caries?
Dental caries is the scientific name for tooth decay. Tooth decay is chiefly caused by the bacteria mutans streptococcus, which produces acid that dissolves and decays teeth, leading to cavities.
The onset of tooth decay is marked by demineralization of the surface of the tooth or teeth. At this stage, it is possible for the decay to heal through remineralization. In general, however, cavities and tooth decay do not heal naturally. Once a cavity has developed, treatment, such as drilling into the tooth and filling the cavity, is necessary.
Cavities do not naturally heal and return the teeth to their original state. They require treatments that can include: removing areas affected by cavity-causing bacteria, applying fillings to the decayed areas, placing crowns, etc.
In essence, once you have tooth decay, it is impossible to return the affected teeth to exactly how they were before. As such, early detection and treatment are important. For About Cavities, Caries, and Tooth Decay that reason, it is vital to take preventive measures such as regular checkups, using fluoride, and undergoing professional cleanings.
Causes of Tooth Decay
-
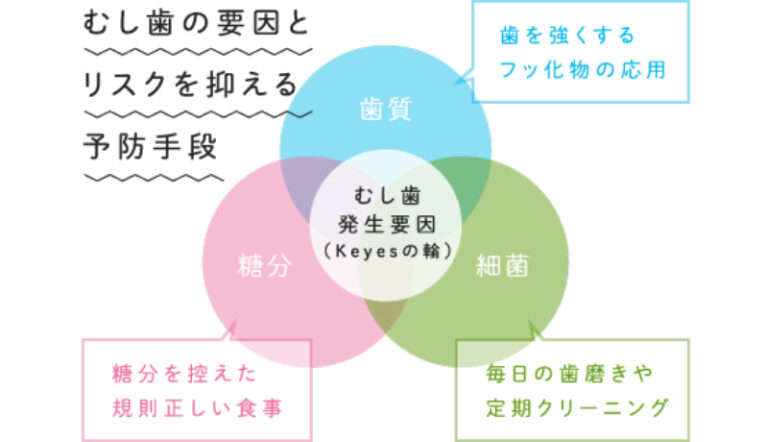
Why do we get cavities?
Tooth decay, and subsequently cavities, develop largely as a consequence of four main factors: bacteria that cause tooth decay, sugar consumption, the teeth themselves, and time. When all these factors compound with each other, tooth decay occurs.
There are of course rare cases of those who have almost no cavity-causing bacteria in their mouths, and consequently do not get cavities even if they skip brushing their teeth occasionally. Likewise, even people who are prone to cavities are less likely to get cavities if they are careful. Avoiding sweets and brushing your teeth immediately after eating are just some of the ways to reduce your chances of developing cavities. It is also important to use fluoride products on a daily basis to strengthen your enamel as much as possible.
Pain Caused by Cavities

What Causes Tooth Pain
Have you ever found yourself wondering, “Why am I sensitive to cold food?” or “Why does eating chocolate hurt?”
The reason cavities and tooth decay cause pain is the nerves inside the tooth. Let’s start by looking at the structure of a tooth.
The visible, white part of your teeth is the hard, inorganic enamel that makes up the surface of your teeth. Inside the enamel is the soft, organic dentin, which contains the nerves of the teeth. When tooth decay progresses beyond the hard enamel, it spreads rapidly through the dentin, which has no resistance to decay. To put another way, enamel is like the armor of the teeth, protecting your teeth and dentin from decay.
-
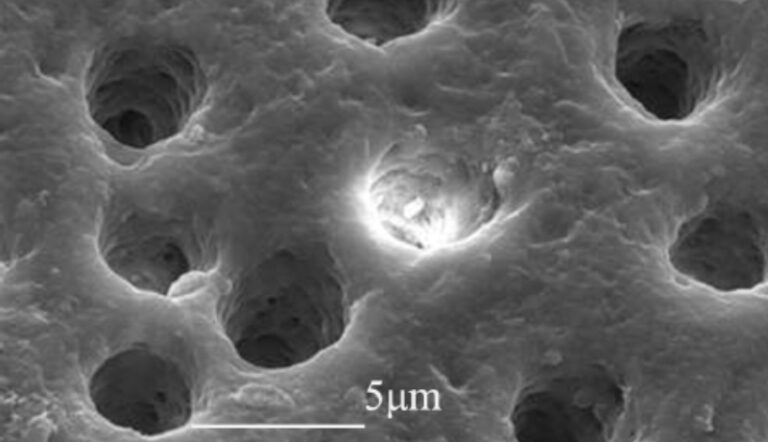
If you look at dentin under a microscope, you can see that it is filled with countless tiny holes. These are thin tubes called “dentin tubules,” and dentin is made up of a vast collection of these thin tubules. The inside of the dentin tubules is filled with liquid, and when this liquid moves due to stimuli such as differences in osmotic pressure, it transmits stimuli to the nerves of the tooth, and this is transmitted to the brain as sensations such as toothache or sensitivity, or other feelings of pain.
Cold drinks and sweet foods such as chocolate can also easily irritate the tissue fluid inside the dentin tubules, causing pain.
Pain During Dental Treatment
-

Dental treatment sometimes involves drilling cavities or removing teeth. The human body responds to such stimuli with pain to tell us that something is wrong.
It is possible to use dental anesthetics to reduce the sensation of pain, allowing dental treatment to be performed without discomfort. In cases of severe nerve inflammation, the anesthetic may not be as effective. In such cases, additional anesthetic is administered so you can complete your treatment without feeling any pain.
Pain Reduction Considerations at Our Clinic
As you might expect, we always use local anesthetics for any treatment that involves drilling into any nerve-filled tooth.
※If you have had any allergies to anesthetics in the past, please let us know in advance.
First, a topical anesthetic is applied to the treatment area, and then a local anesthetic solution is slowly injected using thin anesthesia needles. We always take great care and consideration to minimize pain for our patients during treatment.
■ Topical Anesthetics
Generally speaking, it is not uncommon during dental treatment to begin by immediately injecting an anesthetic with a needle into the treatment area. However, depending on the location of the injection, patients may feel pain when the needle is inserted.
That’s why at our clinic we reduce the pain from the injection by first applying a topical anesthetic (an ointment) to the area. Only then do we inject the liquid anesthetic.
Topical anesthesia works by applying it to the mucous membrane that lines the gums. The mucous membrane absorbs the anesthesia very rapidly, allowing for a mild sense of numbness to set in after about three minutes (some patients may experience the full effect in as little as one minute). Once we’ve confirmed the topical anesthetic has been absorbed, we apply the injection.
■ Electric Anesthesia Administration
As mentioned above, we always administer a topical anesthetic before any procedure that requires anesthesia, in order to reduce the pain of the anesthetic needle being inserted. Incidentally, the pain many patients feel from being administered anesthesia occurs not at the moment the needle is inserted, but when the medication is injected. At our clinic, we always moderate the pressure with which we inject the anesthetic so that patients do not feel any pain. By doing so, we reduce not only the pain of the needle, but also the overall discomfort during anesthesia.
■ 35 Guage Fine Needles
Needles are widely regarded by most as something that have to be painful, especially the needles used for vaccinations and blood draws. It’s no wonder so many people don’t like them! At our clinic, the needles we use at our clinic are 35G thick (0.23mm), which is very thin compared to the needles used for vaccinations and drawing blood (generally around 0.45-0.7mm). With finer needles, there is less pain upon insertion and the flow of the liquid anesthesia is slow and controlled, making it less painful.
■ Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block
At our clinic, we sometimes use an anesthesia technique called “inferior alveolar nerve block”, or IANB, when extracting wisdom teeth. Generally speaking, the bones of the lower jaw are very hard, making it difficult for the anesthetic solution to effectively permeate the bone and allow the anesthetic to work. This anesthesia method directly anesthetizes the area around the nerves responsible for pain signals near the wisdom teeth, By doing so, even patients who are resistant to anesthesia can have their pain reduced and undergo tooth extractions and other dental treatments smoothly.
■ Courteous Service
One factor that makes patients more sensitive to pain is feeling extremely tense or nervous.
We take our time to fully explain our treatments to each of our patients beforehand, answering all of their questions and receiving their informed consent. This allows our clinic to provide an environment where patients to not feel even the slightest bit of tension when they come to us for treatment.
If you have any fears or anxieties about dental treatment, please feel free to consult with our clinic.
Our Measures for Addressing Post-Treatment Pain
Once the anesthetic from treatment wears off, there will be some pain in the treated area. To address this, we will provide you with painkillers. Make sure you take them as prescribed.
It is typical to continue to experience some pain for 2-3 days following treatment. As such, we ask that you continue to take your prescribed medications and monitor the condition of the treated area. There are cases where severe pain in the area will not go away without removing the affected nerve. If you are experiencing severe pain, please contact our clinic immediately.
Preservation-Oriented Nerve Treatment

Cavity tooth pain progresses in stages. The initial symptom of tooth decay is cold foods and drinks starting to sting when you consume them. If the cavity progresses a little further, warm foods and beverages start to sting as well. In many cases, it is still possible at this stage to treat the tooth while leaving the nerves intact. In cases where the cavity progresses too close to the nerve, it often becomes necessary to remove the nerve. Signs that the cavity may be encroaching the nerve include: throbbing sensations in/around the tooth even when you are resting your mouth, feeling pain when you are trying to sleep at night, and tooth pain from the impact of simply walking down the stairs.
Fundamentally, we believe it is important to leave as much nerve tissue as possible intact.
Because removing the nerve increases the risk of bacteria developing inside of the tooth, it can significantly reduce the lifespan of the tooth. As such, even in cases where there is severe pain that ultimately requires removing the nerve, it’s generally better to wait as long as possible before removing it.
The Progression of Tooth Decay
- C1:Enamel Decay
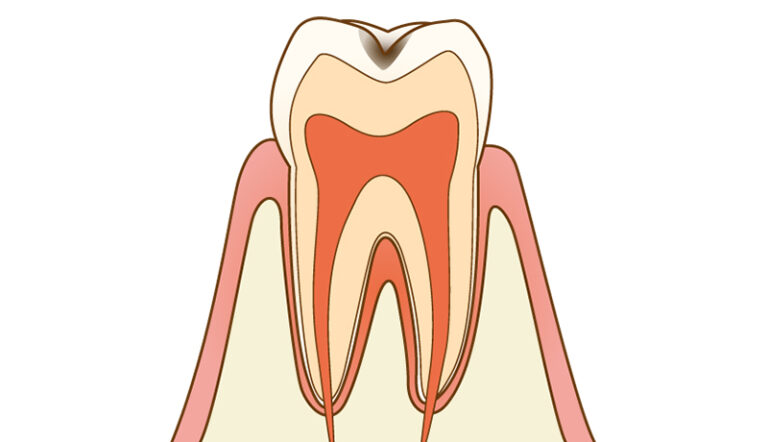 This is the first stage of tooth decay, which is limited to the enamel that makes up the surface of the tooth. There are generally no symptoms at this point, including pain. It’s characterized by parts of the tooth surface turning whiter, while the grooves of the teeth begin turning black and developing small holes. Treatment involves scraping the tooth a little and filling the area with resin (plastic).
This is the first stage of tooth decay, which is limited to the enamel that makes up the surface of the tooth. There are generally no symptoms at this point, including pain. It’s characterized by parts of the tooth surface turning whiter, while the grooves of the teeth begin turning black and developing small holes. Treatment involves scraping the tooth a little and filling the area with resin (plastic). - C2:Decay that has Reached the Dentin
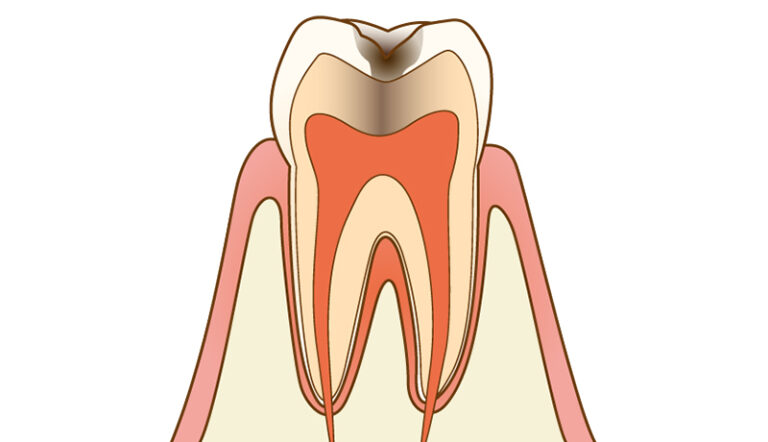 Cavities that have bored through the enamel and into the dentin are called C2. Dentin is mainly made of organic matter, so when cavities reach the dentin, decay progresses very quickly. The symptoms of tooth decay at this stage vary depending on the size of the cavity, but can include: sensitivity to cold, sensitivity to heat, and sensitivity to sweet foods and drinks.
Cavities that have bored through the enamel and into the dentin are called C2. Dentin is mainly made of organic matter, so when cavities reach the dentin, decay progresses very quickly. The symptoms of tooth decay at this stage vary depending on the size of the cavity, but can include: sensitivity to cold, sensitivity to heat, and sensitivity to sweet foods and drinks.
Depending on the location and size of the cavity, treatment will involve either filling the cavity with resin (plastic) or taking an impression of the tooth. This impression is used to create a partial filling, either an “inlay” or an “onlay”, which is later affixed to the tooth. About Aesthetic Dentistry - C3:Decay that has Reached the Tooth Pulp (nerves)
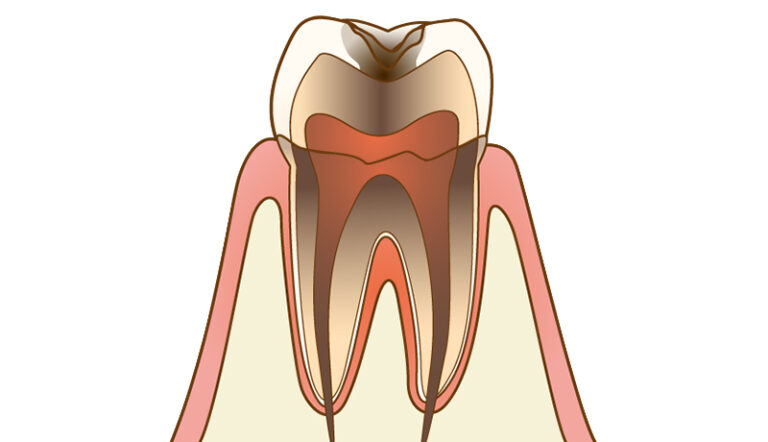 If the decay continues to progress, it will reach the nerve and cause severe pain. At this stage, the symptoms will not improve unless the nerve is removed, so root canal treatment is required. Removing the nerves of the tooth can cause considerable damage to the tooth, so we perform treatment in a manner that preserves as much of the nerves as possible.
If the decay continues to progress, it will reach the nerve and cause severe pain. At this stage, the symptoms will not improve unless the nerve is removed, so root canal treatment is required. Removing the nerves of the tooth can cause considerable damage to the tooth, so we perform treatment in a manner that preserves as much of the nerves as possible. - C4:Decay that has Caused Structural Tooth Loss
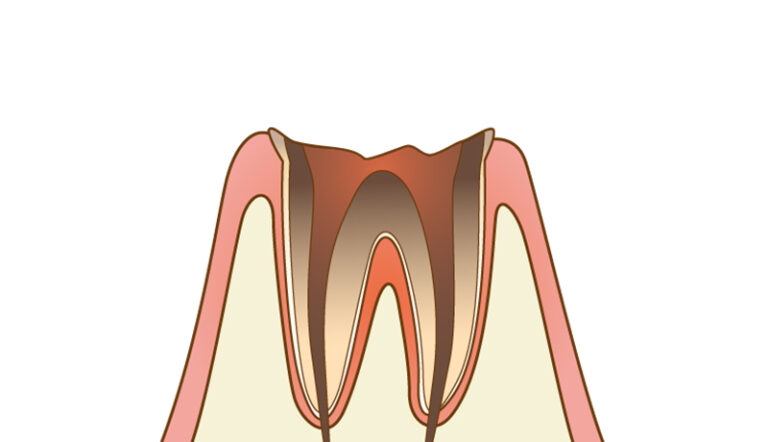 At this stage, most of the tooth has been lost to decay and only the worn-down tooth roots remain. Tooths that have lost their nerves, or have dead nerves, will continue to decay without causing any pain. Because of this, by the time you notice the cavity it may have already progressed to the C4 stage. The treatment for most teeth at this stage is extraction.
At this stage, most of the tooth has been lost to decay and only the worn-down tooth roots remain. Tooths that have lost their nerves, or have dead nerves, will continue to decay without causing any pain. Because of this, by the time you notice the cavity it may have already progressed to the C4 stage. The treatment for most teeth at this stage is extraction.